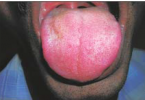
Fibrosarcoma
Epidemiology
This tumor was formerly considered the most common soft tissue sarcoma.
However, with better definition of tumors such as fibromatosis and malignant fibrous histiocytoma (which were previously lumped together with fibrosarcoma), fibrosarcoma now accounts for only 5 to 1 0% of all sarcomas.
This tumor may be seen in all ages, but most of them occur in adults between 40 and 70 years of age.
In children, most tumors are diagnosed in the first year.
Males account for 60% of cases.
These tumors tend to occur in the lower extremities, whereas head and neck lesions account for up to 20% of cases.
Clinical Findings
Patients usually present with a history of a slow-growing mass ranging from months to several years.
The lesion is usually superficially located and feels firm or hard.
Pathology
Grossly, the tumor appears grayish white, firm, and well circumscribed.
Poorly differentiated tumors and tumors in children appear more friable.
In adults fibrosarcomas lend themselves to histologic grading because such grading (well, moderately, and poorly differentiated) correlates with recurrence rate, metastasis, and survival.
However, in children, tumor behavior cannot be predicted from histology.
Treatment
If the tumor is deemed resectable, wide surgical margins should be obtained. The recurrence rate varies between 2 5 and 75%.
Distant metastasis is present in 50% of patients and they are mainly hematogenous.
Tumors that initially present as cervical nodal metastases account for < 1 0% of cases.
This tumor is not particularly sensitive to irradiation although some patients may benefit from a course of radiation therapy following surgery.
The overall 5- and 10-year survival rate is 50 to 60% and the prognosis is more favorable in children
Imaging Findings
CT
On contrast-enhanced CT the tumor shows intermediate density and is usually well circumscribed.
These tumors moderately enhance following contrast administration. These tumors are usually slow growing and rarely aggressively erode.
The bony changes that are present are often due to regressive remodeling. Inrratumoral calcifications are rare
MR
The tumor shows variable signal intensity on both T 1 – and T2-weighted images.
It diffusely enhances following contrast administration.
In some patients T2-weighted images may be hypo intense in signal intensity.
Imaging Pearls
The tumor should be accurately delineated to facilitate wide surgical excision. Tumor affecting the masseter muscle may extend to the suprazygomatic portion of the masticator space .
The diagnosis in an adult can be suggested by a primary masticator space mass that does not demonstrate aggressive bone destruction. The differential diagnosis would include non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, liposarcoma, and inferior extension of a skull base meningioma.
A on the left
B on the right
ــــــــــــــــــــ► ⒹⒺⓃⓉⒶⓁ–ⓈⒸⒾⒺⓝⓒⒺ ◄ــــــــــــــــــــ