Abscess Associated with Odontogenic Infection
Epidemiology
- Dental infection and periodontal inflammation are common infections.
- They may result in mandibular osteomyelitis if appropriate therapy is delayed.
- Septicemia with resultant osteomyelitis is uncommon but may be encountered in the pediatric age group.
- Mandibular osteomyelitis may spread into the adjacent medial pterygoid or masseter muscles resulting in masticator space infection.
Clinical Findings
- Osteomyelitis is associated with pain and fever.
- In addition, patients with masticator space abscess will have varying degrees of trismus.
- Clinical examination will reveal redness and swelling over the face.
- A discharging sinus may also be evident on inspection.
- Masticator space abscess usually occurs from an infected premolar or molar tooth from either the mandibular or the maxillary alveolar ridge
Pathology
- Patients with dental and periodontal disease usually have a history of poor oral hygiene.
- In some patients the underlying cause is previous irradiation for head and neck malignancy.
- The immune system may be further compromised by the institution of chemotherapy.
- The most commonly cultured microorganism is StaphyLococcus. However, a wide variery of anaerobes may also be found.
Treatment
- The treatment consists of appropriate antibiotic coverage, removal of the infected tooth, and drainage of the masticator space abscess.
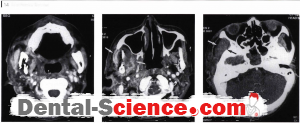
Imaging Findings
CT
- Mandibular osteomyelitis is characterized by osteolysis and erosion of the involved mandible.
- This is associated with adjacent soft tissue swelling in the masseter or medial pterygoid muscle.
- Infections of the mandible may extend deeply into the sublingual space or superficially into the buccal space.
- Phlegmon is characterized by diffuse enhancement of the soft tissues.
- An abscess will have a low attenuation center with enhancement of the surrounding soft tissues.
- Air in the soft tissues may be present if the infection is due to gas-forming organisms
MR
- On T l -weighted M R imaging, the high signal intensiry of the mandibular marrow is replaced with intermediate signal intensiry in inflammatory tissue.
- On T2-weighted images high signals can be seen in the marrow space and soft tissues of the masticator space.
- There is diffuse enhancement of the soft tissue with infections due to phlegmon.
- Abscess will show the characteristic enhancement.
Imaging Pearls
• In the evaluation of patients with a masticator space infection, bone algorithm must be obtained to evaluate for osteomyelitis of the mandibular or maxillary alveolar ridge from an infected tooth.
ــــــــــــــــــــ► ⒹⒺⓃⓉⒶⓁ–ⓈⒸⒾⒺⓝⓒⒺ ◄ــــــــــــــــــــ