Zinc Phosphate Cement
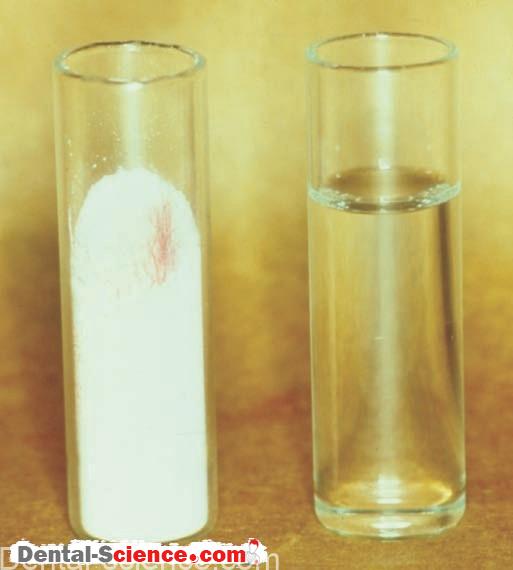
– Zinc phosphate cement is formed when zinc oxide powder is mixed with phosphoric acid.
– Zinc phosphate cement has been used in dentistry for centuries.
– At one time, it was the strongest and least soluble cement that was available.
– This is no longer true, but zinc phosphate cement remains an option for several uses.
A. Products
1. Zinc phosphate cement is supplied by manufacturers as a powder and liquid.
The powder and liquid are mixed to a thick or thin consistency depending on the clinical use.
2. Zinc phosphate cement powder comes in shades.
The color of cement can affect the esthetics of a translucent restorative material.
When a translucent ceramic crown, such as an all-porcelain crown, is cemented, the shade of the cement is chosen to maximize the esthetics of the restoration.
Zinc phosphate cement powder is mixed with water for trial cementing of the restoration.
If the shade is acceptable, the cement is then mixed with cement liquid, and the crown is luted in place.
B. Properties
1. As mentioned, zinc phosphate cement is strong and has a low solubility compared to other cements.
2. Because the mixed cement has a low pH until it has set, zinc phosphate cement is irritating to the pulp.
When zinc phosphate cement is used as a base, often a liner is placed or a varnish is first applied to the preparation.
3. Zinc phosphate cement sets to a hard, brittle material.
It can withstand amalgam condensation forces and support the overlying amalgam
restoration.
Removing excess luting material is very easy if the material is allowed to set and become a brittle mass, after which it breaks off cleanly in large chunks.
If one is impatient, the soft material breaks into little pieces, making removal more difficult.
C. Mixing
1. Zinc phosphate cement is dispensed as scoops of powder and drops of liquid.
A cement spatula and glass slab is used to mix the material.
2. Zinc phosphate cement is mixed to the proper consistency, which depends on the intended clinical use.
The mix is thinner (lower powder/liquid ratio) when used as a luting agent and thicker (higher powder/liquid ratio) when used as a base.
Proper mixing is critical. When improperly mixed, zinc phosphate cement is difficult to
handle and has inferior properties.
3. The setting reaction is very exothermic.
The heat of the reaction accelerates the setting rate.
It is important to dissipate this heat.
Zinc phosphate cement is mixed slowly and over a large area of a chilled glass slab to
dissipate the heat of the setting reaction.
Each increment of powder is mixed for 10 to 15 seconds (for a total of 60 to 90 seconds) to facilitate the transfer of heat to the glass slab.
The chilled glass slab absorbs the heat given off and slows the setting reaction, enabling more powder to be incorporated into the liquid.
Using the entire surface of the slab facilitates heat removal.
The powder is incorporated into the liquid with force, as with ZOE cement.
The significant difference is that the powder for zinc phosphate is added first in small
increments and then in larger ones.
The heat of the reaction of the initial small increments is dissipated into the glass slab if mixing is slow enough.
4. When a luting mix is desired, mixing is continued until a “1-inch string” occurs when tested with the cement spatula.
When a base consistency is desired, a higher powder/liquid ratio is used.
In this case, mixing is continued until the material has the consistency of putty and can be rolled into a ball with fingers covered with cement powder.
If too little powder is used, the mixed mass will be sticky and difficult to handle.
A proper base mix will not stick to powder-covered instruments and can be pushed or
condensed into place.
5. As with all dental cements, the set material is nearly insoluble in water.
Therefore, it is important that the cement spatula and glass slab are washed with tap water before the material sets.
If one delays clean-up, the set material become very difficult to remove from the slab and the instruments.
If the mix happens to set on the spatula or slab, clean-up is much easier if the instruments are soaked in a baking soda–water solution.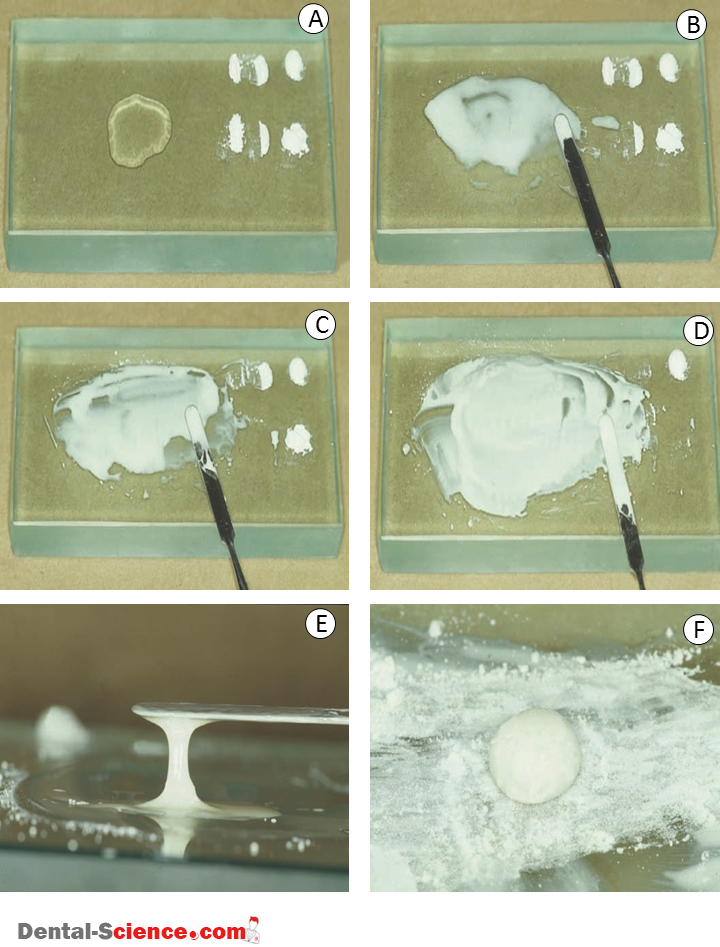
D. Uses
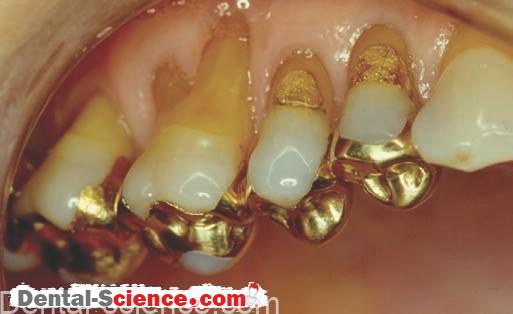
1. Zinc phosphate cement is used for luting inlays, crowns, bridges, orthodontic bands, and other appliances.
Zinc phosphate cement has a long working time compared to other luting cements.
2. Zinc phosphate cement is also used as a base material.
It is acidic, however, and the pulp may need to be protected with a liner or a varnish.
3. Years of clinical use have demonstrated the longevity of zinc phosphate cement.
ــــــــــــــــــــ► ⒹⒺⓃⓉⒶⓁ–ⓈⒸⒾⒺⓝⓒⒺ ◄ــــــــــــــــــــ