Hemangiosarcoma
Epidemiology
- Hemangiosarcomas can arise from endothelial cells in almost any organ.
- The head and neck represent the most common sites for these tumors, and they are predominantly located in the scalp.
- This malignancy is found mainly in the older age group but is also reported in the pediatric age group.
- Males are more commonly affected, with a sex ratio of M:F of 4: 1 .
Clinical Findings
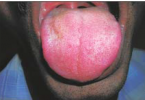
- Most patients present with a mass.
- The lesions appear blue with a peripheral zone of erythema
Pathology
- Hemangiosarcomas can be classified into two groups.
- Low-grade malignancy shows better tumor differentiation, whereas the high-grade variety exhibits poorly or undifferentiated tumor tissues.
- High-grade tumors tend to show wide and deep tissue infiltration, and the adjacent bony structures may be eroded.
- Hemangiosarcomas show cervical nodal or pulmonary metastasis in about one third of patients.
Treatment
- Treatment depends on the site and size of the tumor.
- Surgical excision is the primary form of treatment.
- Radiation therapy can also be used.
- The most important reason for treatment failure is the underestimation of tumor volume.
- The prognosis is generally poor with more than 50% of patients dying within 5 years.
Imaging Findings
CT
- Contrast-enhanced CT shows an enhancing mass.
- There may be associated bony erosion.
- The presence of tumor bleeding may be masked following contrast enhancement.
MR
- Hemangiosarcomas are often hemorrhagic and on T l – and T2-weighted images, high signalsmay be detected.
- The neoplasm shows intense enhancement following the injection ofcontrast. On T2-weighted images, the tumor shows high signals
Imaging Pearls
- The MR and CT findings of hemangiosarcomas are nonspecific but this diagnosis maybe suggested if tumor hemorrhage is detected.
- Hemorrhage on CT may be missed when only contrast-enhanced examinations are performed .
- Tumor size estimation is frequently underestimated clinically and this may result in treatment failure.
- It is therefore important to delineate the full tumor extent
ــــــــــــــــــــ► ⒹⒺⓃⓉⒶⓁ–ⓈⒸⒾⒺⓝⓒⒺ ◄ــــــــــــــــــــ