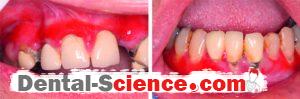
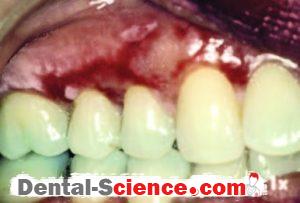
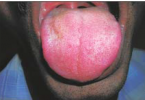
Desquamative gingivitis is a term that describes edematous, red and ulcerated gingiva with a spread of bullous in it. It’s a manifestation, not a disease, so it can be found in many diseases that affect the gingiva.

Before talking at length about desquamative gingivitis, let’s remember what gingiva is and from what it’s composed.
What is Gingiva?
Gingiva is the portion of the oral cavity covering the alveolar bone and the roots of the teeth surrounding their necks and protecting them. It’s divided anatomically to free, attached, and interdental gingiva. The healthy gingiva is coral pink in color, smooth in the texture of exhibits surface stippling, scalloped around the teeth, and doesn’t get affected by brushing or any other actions like mastication.
Signs and symptoms of Desquamative Gingivitis:
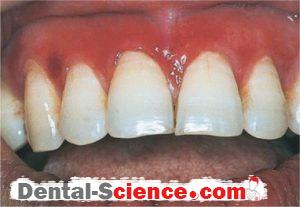
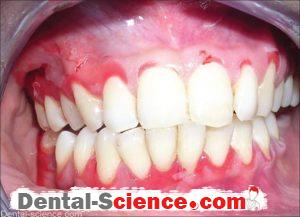
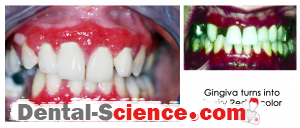
- Gingiva appears edematous with ulcerations affecting both the free and attached gingiva and May also extends into the alveolar mucosa in severe cases, while in the case of plaque-induced gingivitis the inflammation is limited only to the free gingiva.
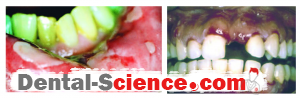
- Desquamation and vesiculation of gingiva that becomes very fragile even in minimal pressure.
- Bullous spreading all over the gingiva. They may rupture after 2-3 days leaving irregularly shaped ulcers that self-heal after 2-3 weeks.
- The color changes from the healthy coral pink to dusky red.
- Desquamative gingivitis is seen in adults more than children, Females more than males, and in the anterior region more than the posterior one.
- In some cases, it can cause severe pain while in some other cases it may be painless.
Causes of Desquamative Gingivitis:
We should note that desquamative gingivitis is a manifestation and a descriptive term, not a diagnosis itself; therefore, it may be a result of many diseases like:
- Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP): is a term that describes a group of autoimmune disorders that affect the mucous membranes of the body, and usually oral mucous membranes especially gingiva is the most affected ones, leading to subepithelial blistering. The scarring of gingiva is the typical characteristic feature of the disease as it’s the first mucous membrane to show the disease. MMP is accompanied by desquamative gingivitis.
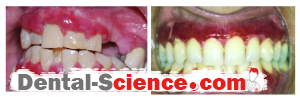
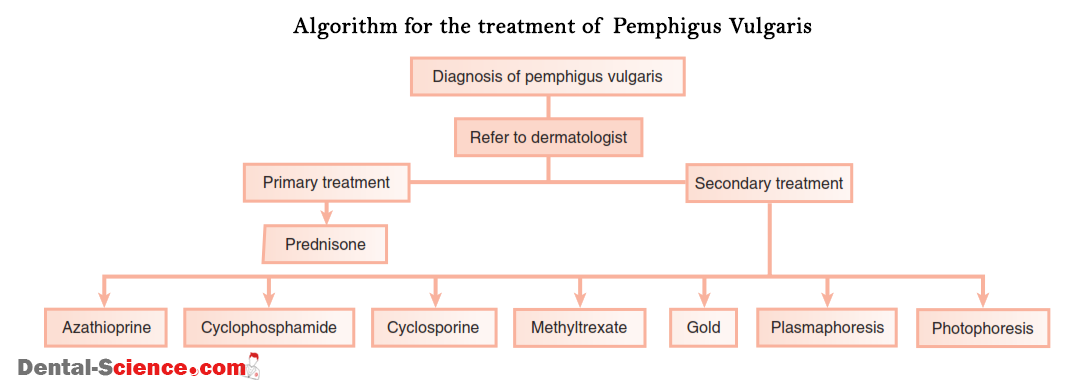
- Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV): an autoimmune life-threatening disease, it hits only the middle-aged patients. PV can affect any mucous membrane but mainly it starts with the oral mucous membranes, causing blisters filled with clear fluid and erosion of gingiva, which are a characteristic of desquamative gingivitis.
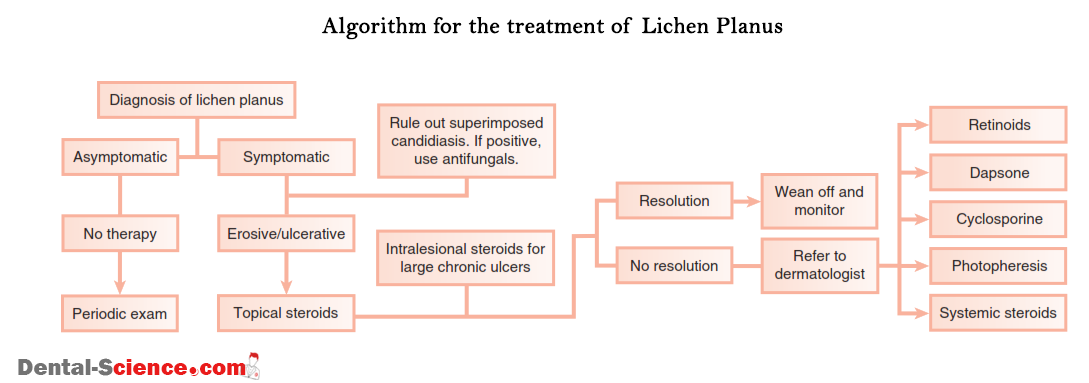
- Lichen Planus (LP): is an inflammatory, non-infectious disease that can affect the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It consists of a rash of bumps that causes itchy or burning sensations in the affected areas. It makes the gingiva inflamed and causes blisters in it.
- The lupus erythematosus (SLE): is an autoimmune disease that attacks the body causing joints pain, skin rashes, and fatigue. One if its oral manifestations are ulcers all over the mouth especially in the gingiva which have the risk of repeated recurrences.
- Dermatitis herpetiformis.
Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis:
It is difficult to reach a final diagnosis of desquamative gingivitis because it is a manifestation of other diseases. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent further complications related to the causing diseases. These diseases may be:
- Oral lichen planus
- Cicatricle pemphigoid or less commonly bullous pemphigoid
- Pemphigus Vulgaris.
- Linear immunoglobulin.
- Dermatitis herpetiformis.
- Lupus erythematosus.
- Chronic ulcerative stomatitis.
- Chronic bacterial, fungal, and viral infections.
- Reactions to medications, mouthwashes, and gums.
- Crohn’s disease.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Leukemia.
Management and treatment of Desquamative Gingivitis:
Fast management should be started as soon as desquamative gingivitis is discovered because most of the autoimmune diseases that cause desquamative gingivitis are life-threatening. There are many factors determine the way of managing the patient, the time of starting immunosuppressive treatment and selection of its type – either topical or systemic- like:
- The disease or disorder that caused desquamative gingivitis.
- The medical history you took from the patient.
- The severity of the gingival distortion.
- The involvement of other mucous membranes.
- Patient’s sensitivity to some types of drugs.
The treatment process is divided into 3 stages:
- Elimination of irrational factors:
- Maintaining proper oral hygiene by brushing the teeth twice a day and using dental floss to avoid the accumulation of plaque which makes the situation worse.
- Prevention of spicy foods and flavors of mouthwashes that irritate the gingiva (caustic mouthwashes).
- Regular use of antiseptic mouthwashes.
- Suppression of the inflammatory reaction
- Treatment of the underlying cause: drugs used for treatment are:
- Corticosteroids:
- Topical corticosteroids (Fluocinonide, Triamcinolone)
- Systemic corticosteroids (Prednisone 10-40 mg).
- Tetracycline.
- Combination of drugs such as Prednisone and Azathioprine.
- Hormonal therapy.
- Photospheres.
Also, recent studies have shown that Desquamative Gingivitis can be treated by the use of free gingival grafts.